It is a tool used by economists to determine whether a good will be in excess or in shortage.
The basic concept behind this law is that if something is expensive, people will buy less of it because they can’t afford it.
Conversely, if something is cheap, people will buy more of it because they can afford to do so.
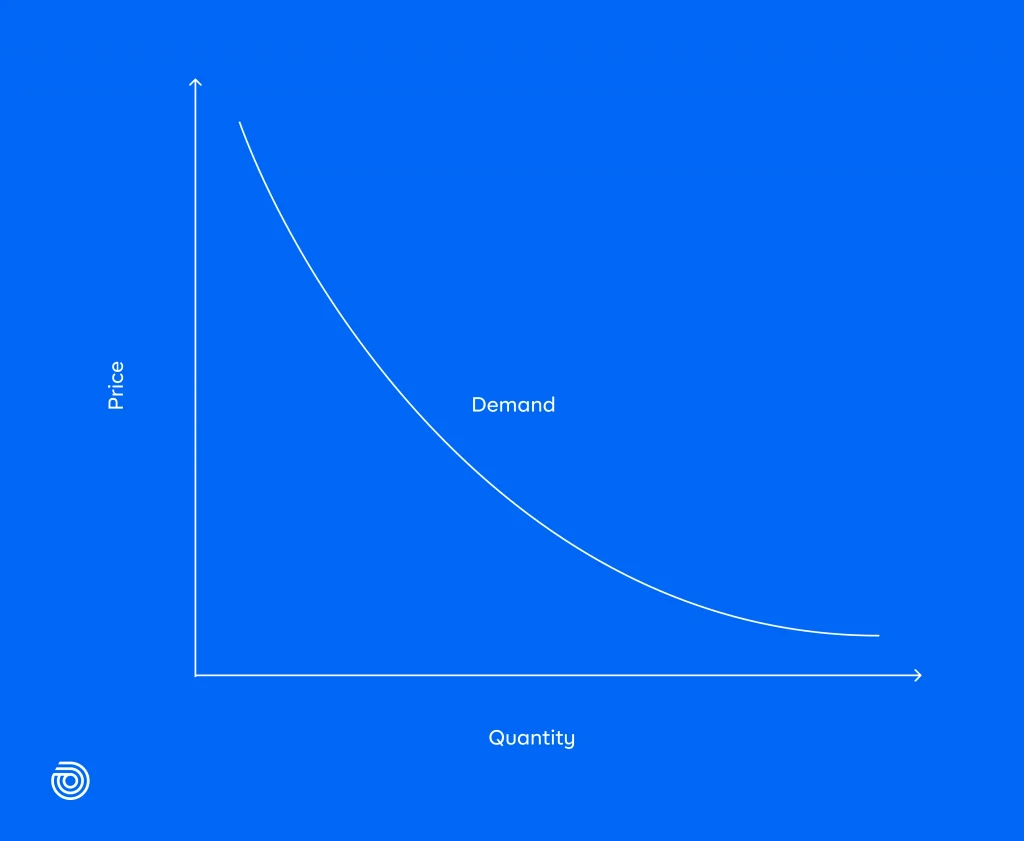
This relationship between price and quantity demanded can be summarized in a graph called a “demand curve”.
Supply and demand in relation to businesses
A company may sometimes reduce its output and raise prices if it expects that demand for its products will decline in the near future.
Companies typically reduce production if they anticipate a decrease in demand or if there’s an increase in production costs (for example because of rising raw material costs).
For example, Apple may reduce the number of iPhones they make if they expect that demand will fall after a new model comes out.
By doing so, they can charge more per unit because there are fewer competitors on the market.
Law of supply
The law of supply states that for a given type of good (homogeneous across both time and space), if the price increases, producers will be motivated to provide more units for sale; if the price decreases, then suppliers will want to sell less.
If other things remain equal, this inverse relationship between price and quantity supplied will continue into the future.
In other words, as long as there are no changes to technology or resources used by suppliers or consumers’ preferences for purchasing goods at different prices and quantities then we could expect that higher prices would lead to increased production while lower prices would lead us toward reduced production.
The law is one of economics’ most fundamental concepts because it describes how markets work: if there aren’t many customers demanding something like milk then suppliers won’t produce much milk either because they can’t make enough money off each bottle sold.
However, once demand increases it creates an incentive for producers who may have been sitting on their hands before now suddenly start producing more milk so they can cash in on higher profits too.
Law of demand
The law of demand states that all else being equal, the higher the price of a good or service, the less people will want to buy it.
The reverse is also true: As prices fall, consumers will be more likely to purchase more goods and services. This can be seen in a number of economic situations.
For example, when fuel prices rise significantly overnight, consumers tend to reduce their consumption (or even stop driving altogether) until the price falls back down again—and sometimes richer consumers may even start buying larger cars with better fuel economy.
Another example might be when you’re shopping online for dinnerware on Jumia and suddenly notice all their dinner plates are 30% off because they’re having a sale on them right now—you’ll probably change your mind and buy more just because they’re cheaper than usual.
Equilibrium Price
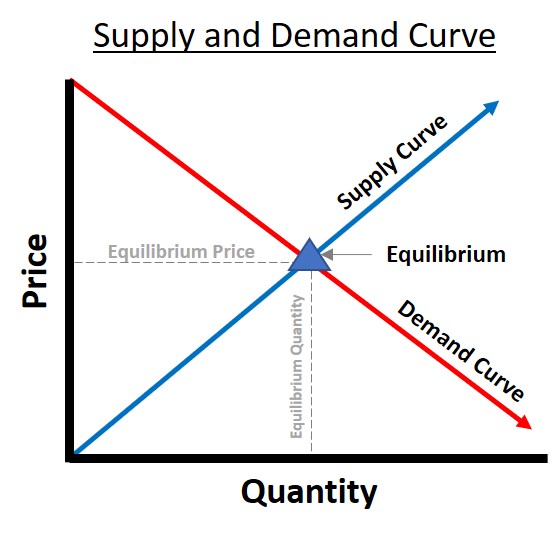
In economics, a specific area on the graph above shows where there is only one price at which vendors will sell their goods and services and where purchasers are willing to pay that price.
The point where the two curves meet is called equilibrium.
At this point, a market tends to be stable and at an equilibrium price.
Factors affecting the law of supply and demand
The law of supply and demand is affected by several factors such as:
- availability of substitutes
- cost-of-production such as labour costs or raw materials used in manufacturing
- consumer preferences for different products or services based on brand loyalty and quality standards
- changing technology trends which could make certain products obsolete over time
- even weather patterns can play an important role when it comes down to what crops farmers choose to plant (or not plant).
Conclusion
The law of supply and demand is an economic principle that explains how prices are determined in a market economy. It states that when the supply of a product increases, its price goes down, and if demand increases, the price goes up.
Learn more about finance
No matter your level of financial literacy, we have more than enough financial education resources to get you started. Also, with our wealth management app, you can easily save, invest, and begin your own path to financial independence.
Related Articles:
Commodity Trading In Nigeria: Everything You Need To Know